Replication?
Replication provides redundancy and increases data availability. With multiple copies of data on different database servers, replication provides a level of fault tolerance against the loss of a single database server.
— MongoDB Manual
A replica set in MongoDB is a group of mongod instances that maintain the same data set. The mongod instances are known as nodes. Nodes could be primary or secondary.
By default write operations are performed on the primary node and synced to other secondary nodes. Read operations are also performed on the primary node by default but the configuration on read operations can be changed.
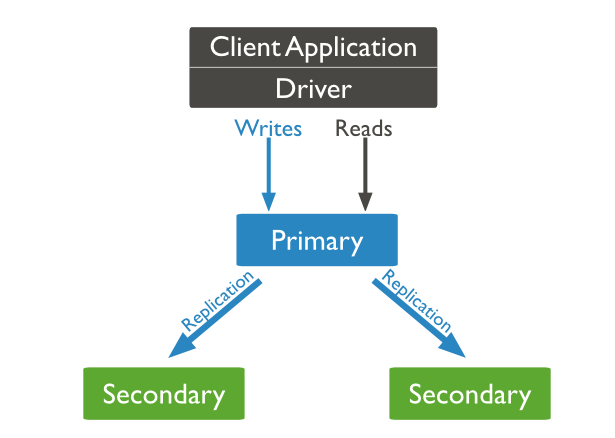
Benefits of replication
- High availability & redundancy
- Distributes database requests, therefore, could increase application’s speed (has to be configured)
Setting Up a Replica Set
-
Set Up MongoDB on the servers :
Mongod instances need to be setup on the servers you plan to use in the replica set.
Ideally, a replica set is to have an odd number of mongod instances; this is to ensure that during an election for a master mongod instance, quorom can be reached. If you can only set up even mongod instances, then you have to add an arbiter. The minimum number of mongod instances is three, if you can only setup two, then you have to add an arbiter.
Arbiters are mongod instances that are part of a replica set but do not hold data. Arbiters participate in elections in order to break ties.
I have seen a few cases where all mongod instances of a replica set are setup on a single server, I think it beats the purpose of setting up a replica set. If that server goes down, then your MongoDB server becomes unavailable.
-
Check connection between Mongod instances :
The connection between the Mongod instances on the different servers needs to be tested and confirmed. This is important if you use a firewall on your servers. I have had cases where I setup a replica set and it wasn’t working only to find out the connection port between the Mongod instances was blocked.
The hostname of the servers where other Mongod instances are located needs to be added to each server’s
/etc/hosts. For a server with hostnameidarlingtonand ip192.168.2.218, it should be added as :192.168.2.218 idarlington -
Set up configuration file :
After confirming the connection between the Mongod instances, you can now begin the replica set setup proper. You need to edit the MongoDB conf file that starts the Mongod service.
For most linux systems the conf file is located in the
/etc/init. For MongoDB 2.4 and lower, the file ismongodb.confwhile for MongoDB 2.6 and above, the file ismongod.confFor MongoDB version 2.6 and above
replication.replSetName : "replset name you have chosen"OR
replication: replSetName : "replset name you have chosen"For MongoDB 2.4 and below
replSet = "replset name you have chosen" -
Initiate Replica Set :
You can now exit the conf file and start a mongo shell on the server you want to be the primary node.
MongoThen to initiate the replica set :
rs.initiate()To show the configuration of the replica set :
rs.conf()To show the recent status of the replica set :
rs.status() -
Add other members :
After initiating the replica set, its only member is the current server where you are running the mongo shell. To add other members to the replica set, use the IP address or hostname of the server with the mongod instance you want to add like
rs.add("192.168.2.128") -
Adding an arbiter :
Arbiters are useful when you have an even number of nodes, if you already have an odd number of nodes, it is not needful. To add an arbiter, you can either use its hostname or ip address.
rs.addArb("192.168.2.13")
Notes
- If you formerly built your application to work with a standalone MongoDB server, you have to update your mongodb connection to work with a replica set. The way to do this differs with the ORM or driver you use for your application.
- You can set read preference on your application. The available options are
primary,primaryPrefered,secondary,secondaryPrefered,nearest.